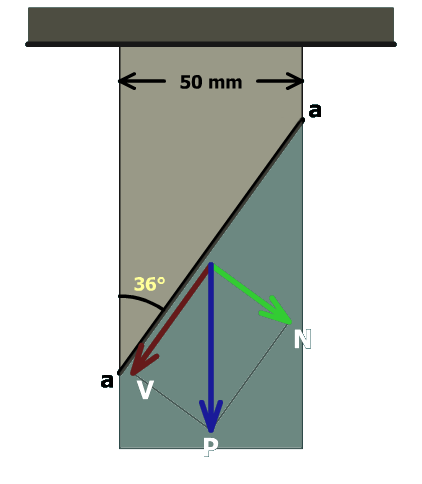
The area of the inclined plane must be determined before the forces acting on section can be computed. The bar width is . Use the angle to compute the length of the inclined surface:
The bar is thick; therefore, the inclined plane area is:

The area of the inclined plane must be determined before the forces acting on section can be computed. The bar width is . Use the angle to compute the length of the inclined surface:
The bar is thick; therefore, the inclined plane area is: