Several measurements are made before, during, and after the test.
Before the test:
• The cross-sectional area of the specimen must be determined. The area will be used with the force data to compute the normal stress.
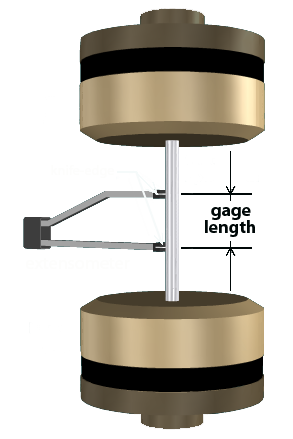
• The gage length of the extensometer should be noted. The normal strain will be computed from the specimen deformation (i.e., the axial elongation) and the gage length.
During the test:
• The force applied to the specimen is recorded.
• The elongation in the specimen between the extensometer knife-edges is measured.
After the specimen has broken:
• The area of the cross section at the fracture location is measured. The reduction in area (between the area of the fracture surface and the original cross-sectional area) divided by the original cross-sectional area provides one measure of the ductility of the material. The term ductility describes the amount of strain the material can withstand before fracturing.