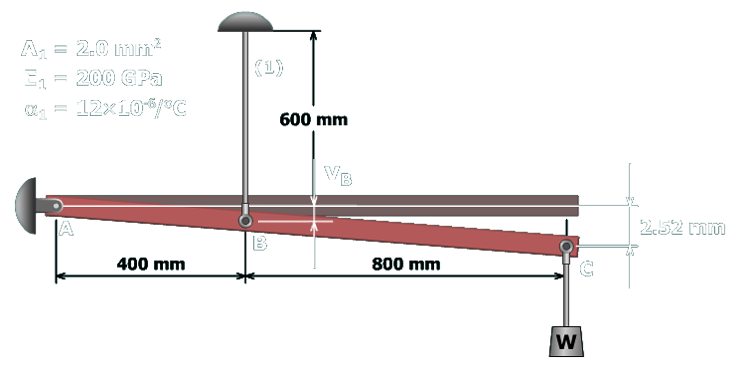
To determine the normal strain in wire , the deformation in the wire must be determined. Since the wire is attached to the rigid bar, the deformation of the wire will equal the rigid bar deflection at point .
The rigid bar remains perfectly straight when it deflects. Therefore, the deflection at can be determined, using the principle of similar triangles, from the measured rigid bar deflection at .