The transverse shear force V will create a shear stress τ that acts in the x-y plane. Since B is near the centroidal axis and on the web of the wide-flange shape (where the thickness t is small), the shear stress τxy at B could be significant.
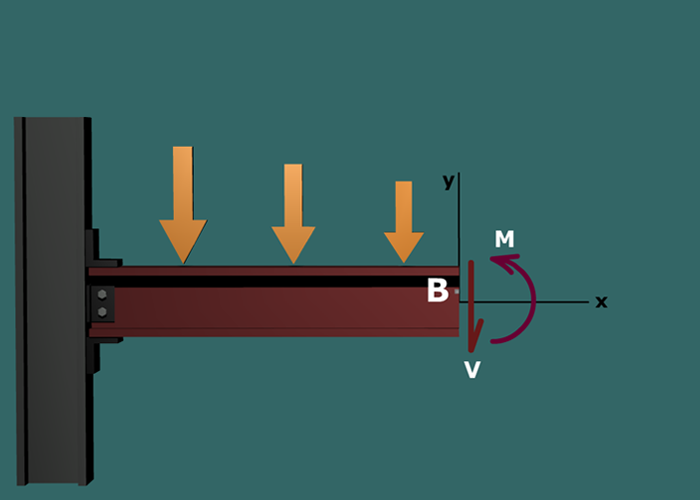
The bending moment M will create normal stress σ that acts in the x direction. The magnitude of σx varies linearly over the depth of the shape (i.e., in the y direction). B is above the centroidal axis and the bending moment is positive; therefore, the normal stress σx at B will be compression.
To calculate τxy and σx at B, the moment of inertia I and the first moment of area Q at point B must be determined.