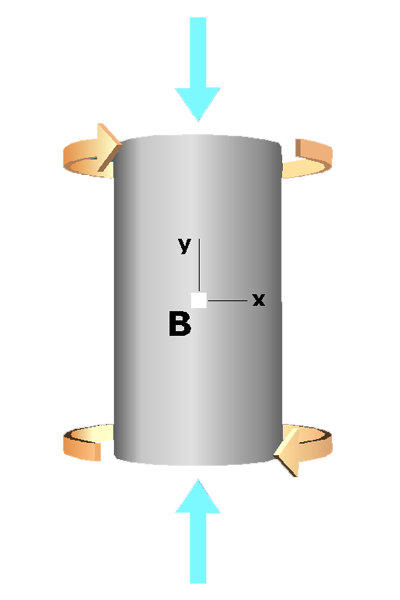
The axial force will compress the shaft, creating a uniform normal stress given by:
where is the cross-sectional area of the shaft.
The torque will twist the shaft, creating a shear stress given by:
where is the outside radius of the shaft and is the polar moment of inertia.
After computing and , we will use Mohr's circle to determine the principal stresses and the maximum shear stress at .