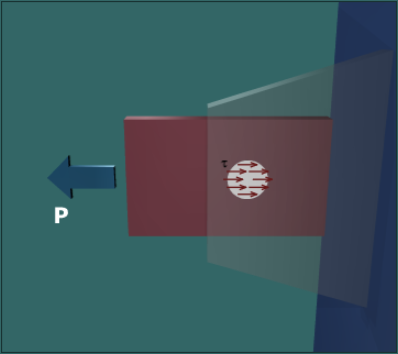
The shear stress acts on a single surface. (If the load was large enough to break the pin, it would break on only one surface.) The area subjected to shear stress in this instance is simply the cross-sectional area of the pin.
Note that the surface upon which the stress acts is parallel to the direction of the applied load ; hence, the term shear stress.