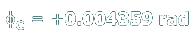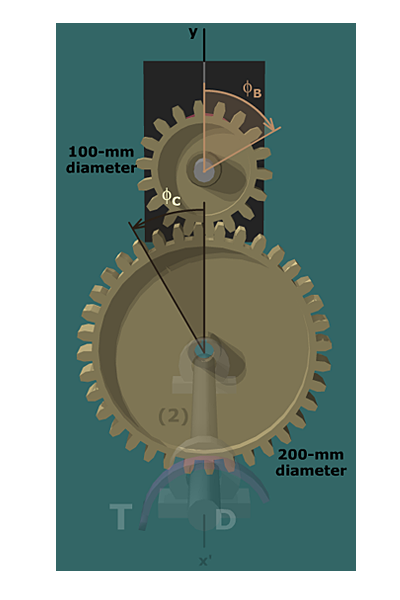
Let's review the rotations in the system, looking from another viewpoint:
When gear B rotates clockwise (negative in our coordinate system), it causes gear C to rotate in a counterclockwise direction (positive). The rotation angle of gear C is half as much as φB because gear C is twice as big (in diameter) as gear B.