M10.1: Beam Boundary Condition Game
Game
Determine appropriate boundary conditions necessary to determine beam deflections using the double integration method.
M10.2: Beam Deflections by Integration Method
Interactive example
Use the double integration method to determine slope and deflection equations for a cantilever beam with a concentrated load at the tip.
M10.3: 8 Skills - Part I
Theory | Concept Checkpoints
Series of skills necessary to solve beam deflection problems using the superposition method.
M10.4: 8 Skills - Part II
Theory | Concept Checkpoints
Series of skills necessary to solve beam deflection problems using the superposition method.
M10.5: Superposition Warm-Up
Example | Concept Checkpoints
Examples and concept checkpoints pertaining to four basic superposition skills.
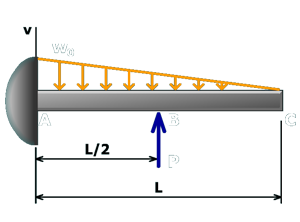
M10.6: One Simple Beam, One Load, Three Cases
Concept Checkpoints
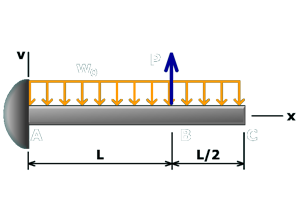
Determine beam deflections at various points in a simply supported beam with two overhangs. All deflections can be determined with superposition of no more than three basic deflection cases. Numeric values rather than symbolic variables.
M10.7: Beam Deflections by Superposition
Example
Introduction to the superposition method. Two of the most basic examples — one simply supported beam example and one cantilever beam example.
M10.8: Cantilever Beam with Two Point Loads
Example
Use both slope and deflection equations to compute deflection at cantilever tip.
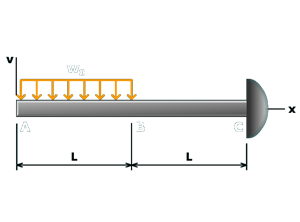
M10.9: Cantilever Beam with Linear Loading
Example
Determine deflection using both upward and downward deflection cases.
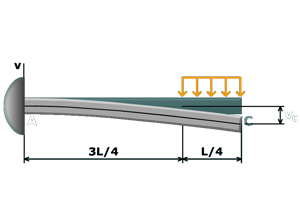
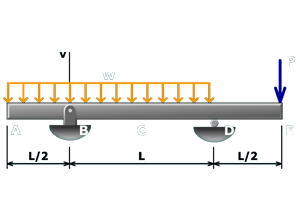
M10.10: Simple Beam with Overhang
Example
Use both simply supported and cantilever beam equations to determine slope and deflection at the free end of the overhang.
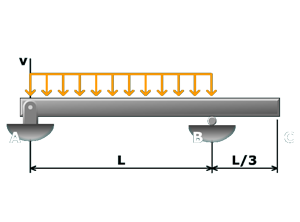
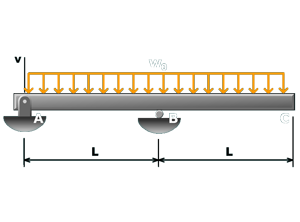
M10.11: Simple Beam with Two Overhangs
Example
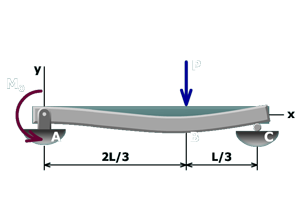
Use simple and cantilever beam equations to determine deflection in the middle of the simple span.
M10.13: Computing Forces from Known Deflections
Example
Determine the force magnitude required to make the beam deflection equal a specified value.
M10.14: Computing Moments from Known Slopes
Example
Determine the moment magnitude required to make the beam slope equal a specified value.