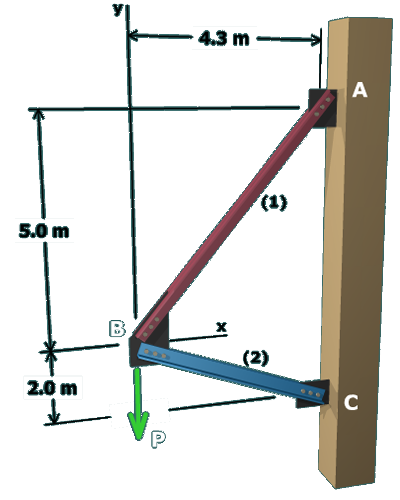
A trial-and-error approach can be used to determine the maximum allowable load :
1. Using the allowable stresses given, compute the allowable axial forces for
members (1) and (2) from:
2. Arbitrarily assume that one of the two axial members will control the load-carrying capacity of the structure. For example, assume that member (1) will be stressed to its allowable limit. If this assumption is correct, member (2) should carry less than its allowable stress.
3. Set and solve the two equilibrium equations simultaneously for the unknown forces and .
4. Compare the value of computed from the equilibrium equations to its allowable force .