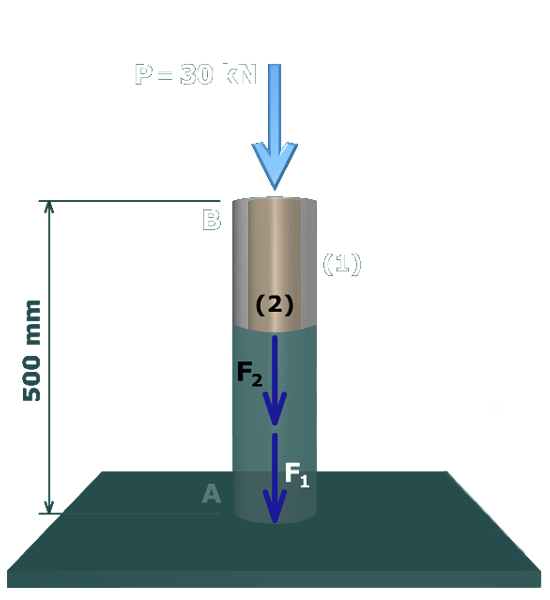
Next, consider the overall geometry of the structure and how that geometry dictates the deformations that can occur.
Since the tube and the core are bonded together, they must deform exactly the same amount. In terms of the deformations, this relationship can be stated as:
This equation is called the geometry of deformations equation.