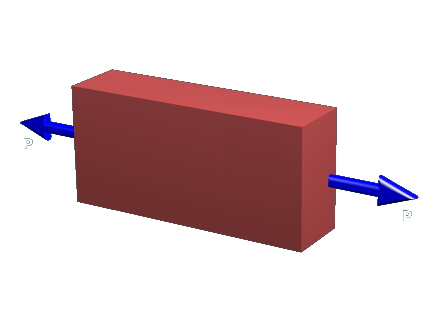
We will consider a very simple object, an axially-loaded prismatic bar, to investigate the nature of stress. The load acts through the centroid of the bar.
While we may be tempted to think that there is only one stress in a material (particularly in a simple axial member), this study will demonstrate that there are many different combinations of normal and shear stress in a material. The magnitude and direction of the normal and shear stresses at any point in a solid material depends upon the orientation we choose.