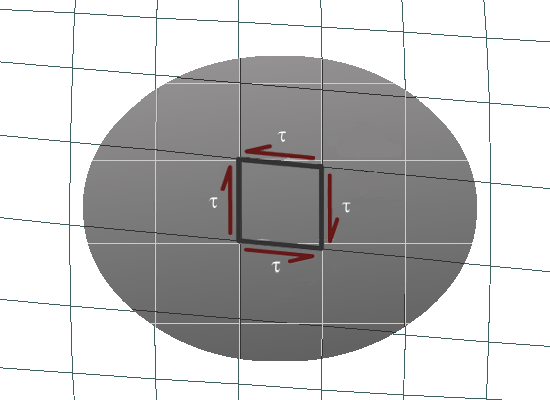
The magnitude of the shear stress that corresponds to the maximum shear strain can be determined from the stress-strain relationship for the material.
Hooke's Law for shear is . Multiply the preceding relationship by ...
and apply Hooke's Law to produce the relationship that describes the variation of shear stress over the cross section.
As with the shear strain, shear stress in a circular shaft varies linearly with the radial distance from the centerline. The shear stress is zero at the centerline and increases linearly until it reaches a maximum value on the outermost surface of the shaft.